Tree
Tree는 Graph의 일종, Acyclic graph
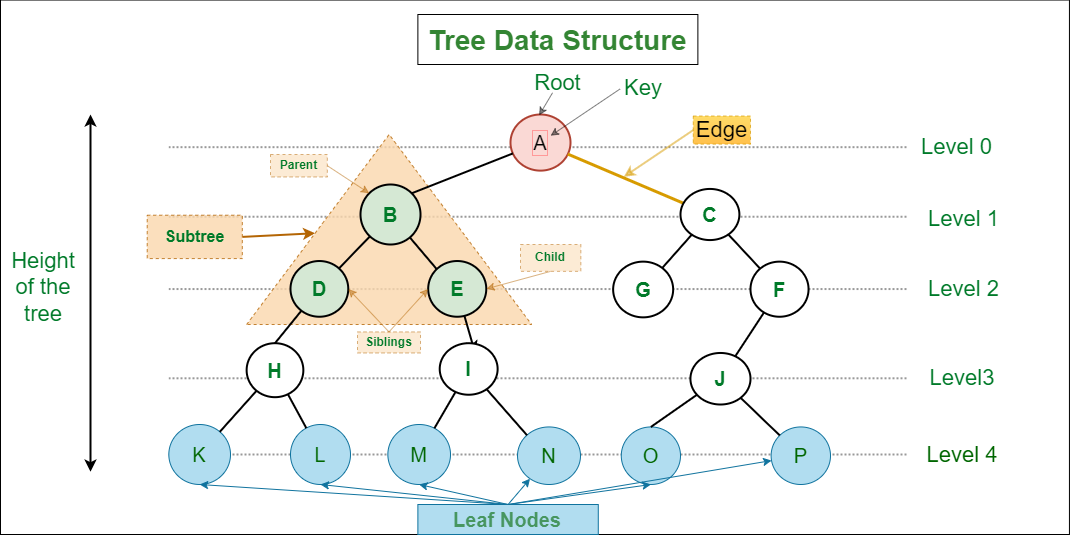 source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-to-tree-data-structure-and-algorithm-tutorials/
source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-to-tree-data-structure-and-algorithm-tutorials/
트리 종류
Binary Tree -> Binary Search Tree -> Self-balancing binary search tree (AVL tree,B-tree,Red–black tree etc.)
Full Binary Tree (완전이진)-> Complete Binary Tree (전이진)-> Perfect Binary Tree(포화이진)
탐색방법
1.DFS Depth-First Search
Root부터 leaf까지 모든 루트를 하나씩 탐색하는 방법
모든 경로를 한번씩 거치기 때문에 경로의 특이점을 저장해둘수 있다
미로찾기 문제로 많이 나온다
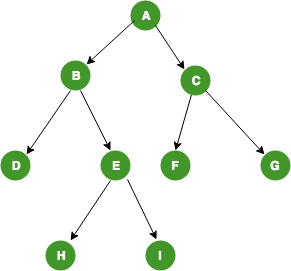
Preorder Traversal, 전위 순회 (Root -> Left -> Right)
root가 첫번째로 와서 전위순회 A-B-D-E-H-I-C-F-G
Inorder Traversal, 중위 순회 (Left -> Root -> Right)
root가 중간에 와서 중위 순회 D-B-H-E-I-A-F-C-G
Postorder Traversal, 후위 순회 (Left -> Right -> Root)
root가 마지막에 와서 후위 순회 D-H-I-E-B-F-G-C-A
외우는 순서는 간단하다. 무조건 Left -> Right. 전위면 Root를 앞에, 후위면 뒤에, 중위면 가운데
DFS 구현방법
stack을 주로 사용, 또는 recursive
2.BFS Breath-First Search
한 레벨씩 훑어가는 방법
최단거리 구하기 문제에 자주 사용된다

구현방법
Queue를 이용해 구현
표현방법
List
use std::{rc::Rc, cell::RefCell};
#[derive(Debug)]
pub struct TreeNode{
pub val:i32,
pub left:Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right:Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>
}
impl TreeNode{
pub fn new(val:i32) -> Self{
TreeNode { val, left:None, right:None }
}
}
fn main() {
let root= Some(
Rc::new(
RefCell::new(
TreeNode::new(1)
)
)
);
let left= Some(
Rc::new(
RefCell::new(
TreeNode::new(2)
)
)
);
let right= Some(
Rc::new(
RefCell::new(
TreeNode::new(3)
)
)
);
let r = root.unwrap();
r.borrow_mut().left=left;
r.borrow_mut().right=right;
}
Array
#[derive(Debug)]
pub struct Array{
pub root:i32,
pub nodes:[Option<i32>;100],
}
impl Array{
pub fn new(val:i32) -> Self{
Array {
root:val,
nodes:[None; 100]
}
}
pub fn left(&mut self,val:i32,parent:usize){
let t = (parent * 2) + 1;
self.nodes[t]=Some(val);
}
pub fn right(&mut self,val:i32,parent:usize){
let t = (parent * 2) + 2;
self.nodes[t]=Some(val);
}
}
fn main() {
let mut arr = Array::new(0);
arr.left(1,0);
arr.right(2,0);
arr.left(3,1);
arr.right(4,1);
arr.left(5,2);
arr.right(6,2);
}
참조: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/binary-tree-array-implementation/